Part 1
· Example: Blink it Up: verify and upload,
and confirmed the light is blinking.
· Example4_Serial: change the baud to
9600, verify, and upload.
· Example4_Serial: switch the serial
monitor’s baud speed to 115200 baud, verify, and
upload:
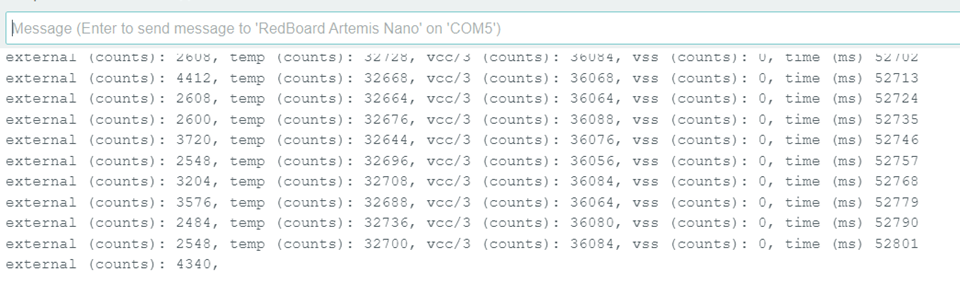
after holding the board in hand
for 60 seconds, temp increased significantly:
·
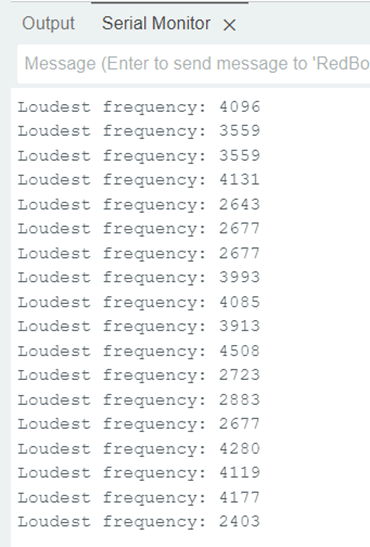
Example1_MicrophoneOutput:
switch the serial
monitor’s baud speed to 115200 baud, verify, and
upload:
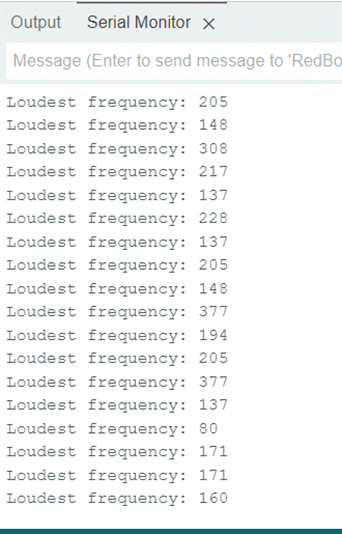
Scratch
on the board, the sound’s frequency became:
Part 2
Goal
Understanding
that Artemis can use Bluetooth to communicate with computer in terms of
Characteristics; There’re multiple Characteristics,
such as float Characteristics and string Characteristics. We can use ble.receive_string(uuid) to
receive a known message, but in lots of cases we don’t
know if there is a message await us, so it’s better to
use ble.start_notify(uuid, notification_handler), which continuously listen to
messages from the given uuid.
Prelab
Following the instructions in Lab1
course page, running following commands in powershell
to get the environment ready:
python
-m pip install --user virtualenv
python
-m venv FastRobots_ble
For the older computer with both python 2 and 3, use ‘python3’ instead of ‘python’.
Once we have the environment, next is
activate the Virtual environment by
.\FastRobots_ble\Scripts\activate
And install Juypter
Notebook with
pip
install numpy pyyaml colorama nest_asyncio bleak jupyterlab
Then simply put the given codebase into
the environment, we are ready to start tasks.
·
T1 Send
ECHO command
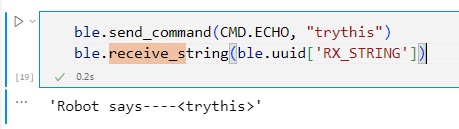
·
T2.
Programming and use GET_TIME_MILLIS command

·
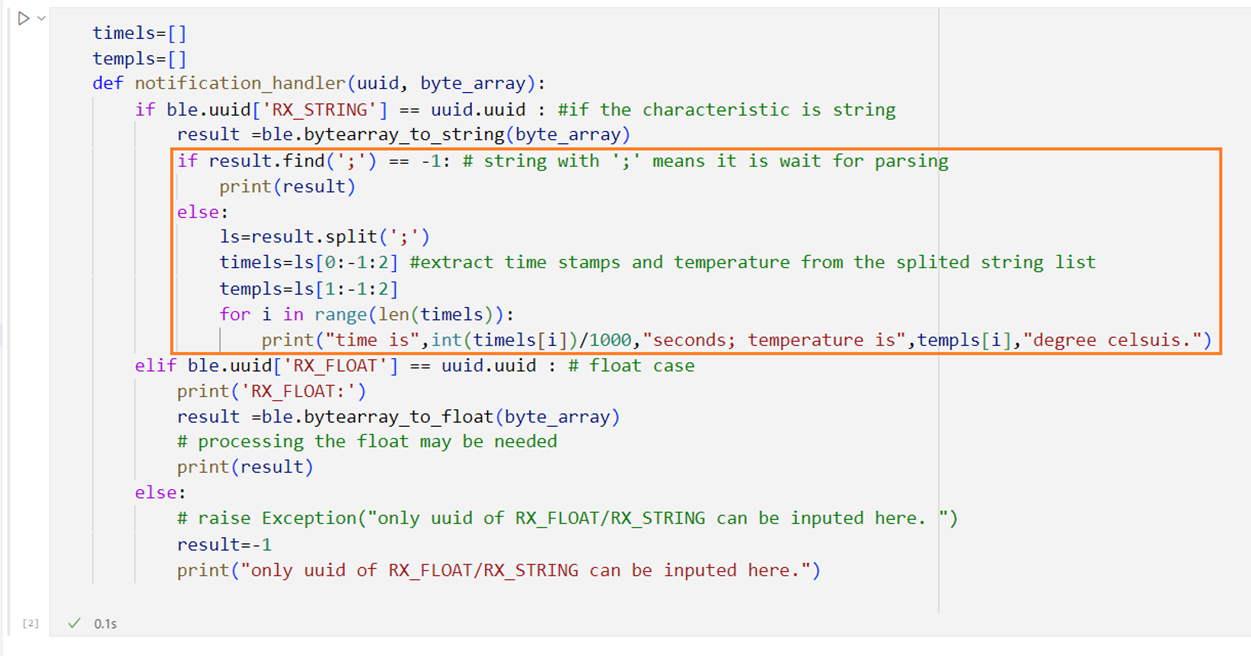
T3.
notification handler
After
setting up the notification handler, once Artemis send a message, Juypter notebook will immediately receive it and print in
on screen; I used 1 if condition to determine incoming characteristic is string
or float, another nested if condition for the time stamp and temperature
extraction for later tasks.

For example, once CMD.GET_TIME_MILLIS lets the Artemis send the current time “T:215108.0”, Juypter
notebook receive and print it.
·
T4. Get current time stamps
I implemented a function in ble_arduino
to send 100 time stamps. I didn’t choose larger amount
of time stamps to avoid running of memory.
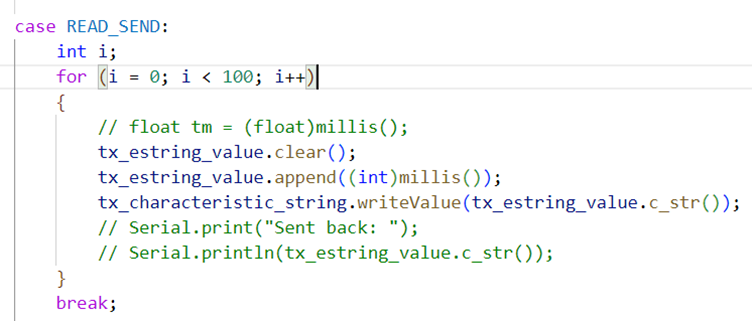
And when
I sent the commend from python, 100 results are sent back from Artemis:

Average
data transfer rate = 47.755 strings/s = 334.3 bytes/s
·
T5. Get, store, and sent
time stamps--SEND_TIME_DATA command
I implemented a function in ble_arduino
to send 105 time stamps. I used 15*7 nested loop instead of 105 loop to
overcome the Estring size limitation problem: in this
case, the length of the Estring tx_estring_value
is ensured to be less than 150 before I clear its content;
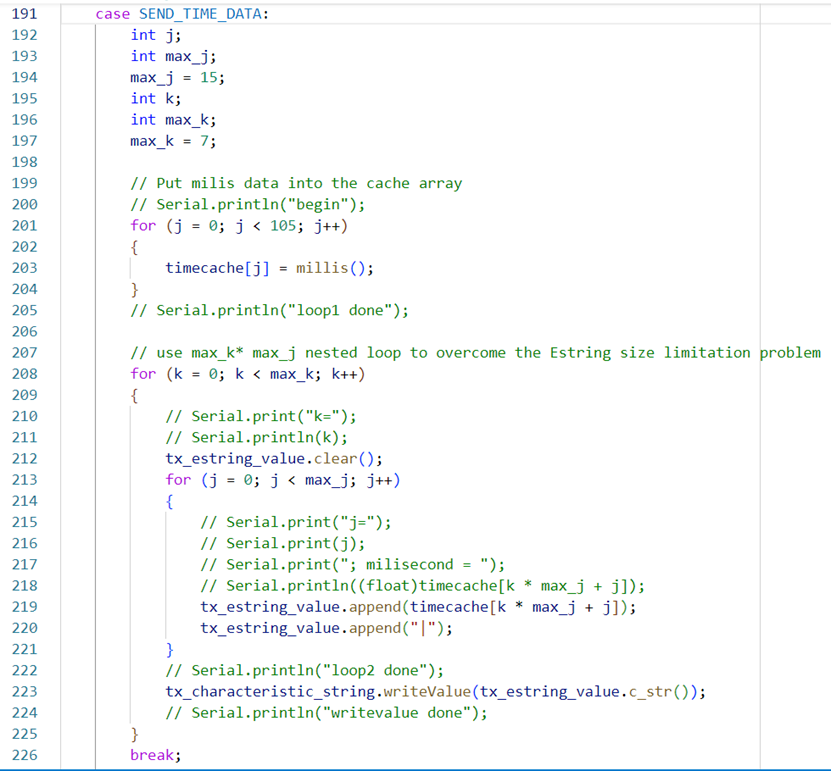
And when
I sent the commend from python, 105 results are sent back from Artemis:
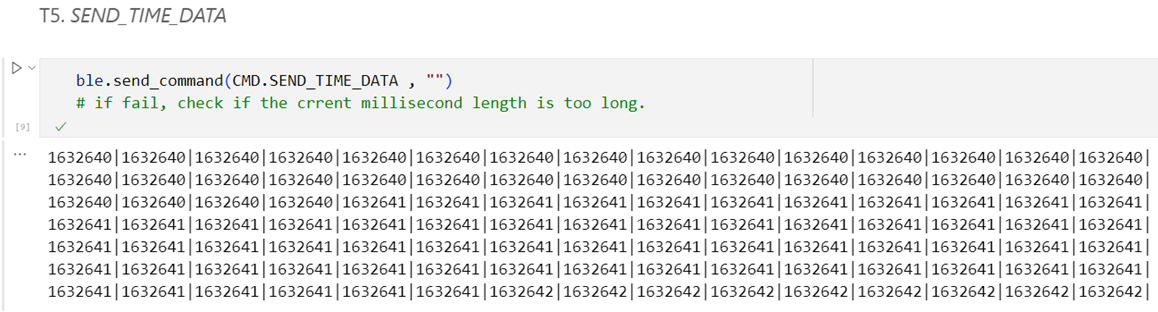
Average
data recording rate = 52500 strings/s = 420000 bytes/s
·
T6. Send time& temperature--GET_TEMP_READINGS
Added a
nested if condition to extract time stamp and temperature from the string characteristic.
I chose ‘;’ as delimiter
because it’s not used in the raw data.
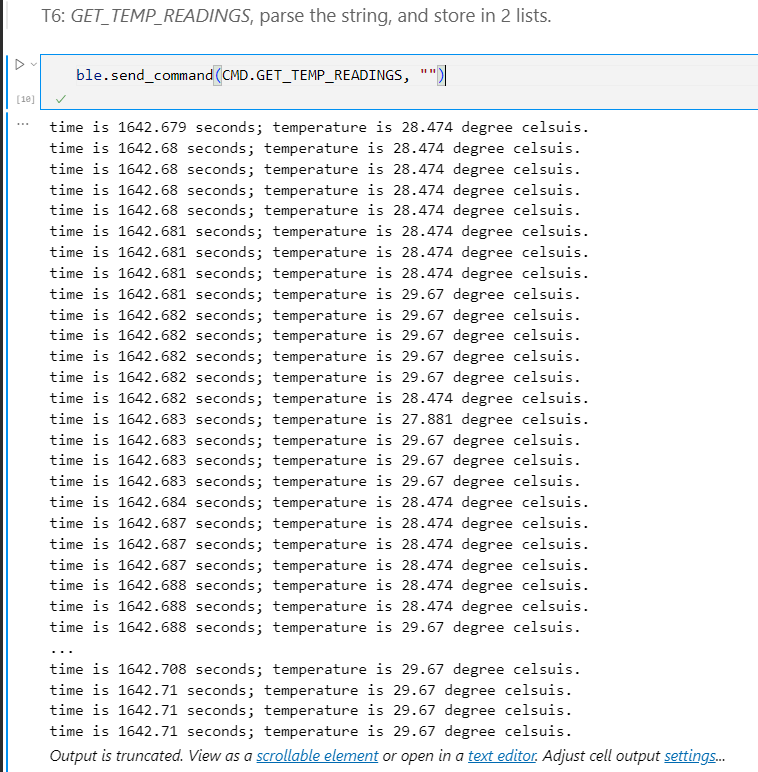
Average
data recording rate = 3225.8 strings/s = 48387.1 bytes/s
·
T7. Compare and Contrast
The
first method(sending while reading data) is more than 1000 slower than the
second method(recording all before sending data). If the memory of the board is
very limited, the first method could be the preferred option; Otherwise, the
second method is better since robots’ data are
time-sensitive and a faster rate is desired in general.
386kB of
RAM means the red board can store 48250 time stamps (assume time is 7 bytes
long and delimiter is 1 byte long) or 55143 temperature readings (assume the
reading is 6 bytes long and delimiter is 1 byte long).
Conclusion, Challenges, and Solutions
1.
When I try to implemented
the notification handler, I didn’t realize that the uuid passed into the handler is GATT Characteristic rather
than string, and that the way to get the string uuid
is to uuid.uuid instead of uuid.uuid(),
as .uuid is defined as a property, not a function;
after reading forum and asking in Ed, I find these facts, and successfully implemented
the notification handler which is able to deal both float and string.
2.
On task 5, my original
codes was not able to print out anything except crush the programming and
disconnect the board; after printing out values inside the loops, I realized
that it’s caused by the 150 transmission length
limitation; I resolved that by using a nested loop.
·
Through these tasks, I
have successfully built up the Bluetooth connection between Artemis board and computer,
enable the GATTCharacteristic data transmission, and found
the limitation of Artemis’s transmission speed & storage.